Who Is The Ideal Candidate For TAVI? Understanding Eligibility & Benefits
02/21/2025
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) has revolutionized the treatment of severe aortic stenosis, especially for patients who are high-risk candidates for traditional open-heart surgery. This minimally invasive procedure offers a lifeline to many, but determining who stands to benefit the most is crucial.
What is TAVI and How Does It Work?
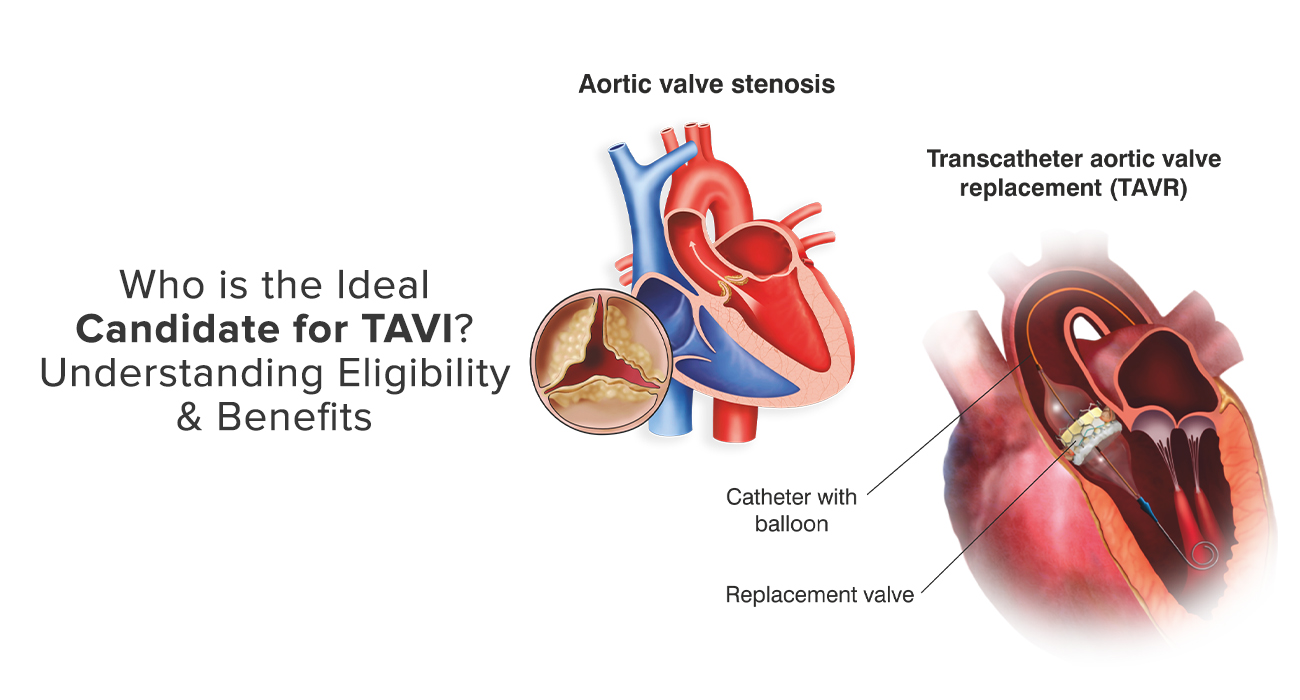
TAVI, also known as Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR), is a procedure designed to replace a narrowed aortic valve that fails to open properly—a condition known as aortic stenosis. Instead of opening the chest to replace the valve, doctors insert a new valve via a catheter through a small incision, usually in the groin. This new valve then takes over the function of regulating blood flow from the heart to the rest of the body.
Read Also: An Overview of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation TAVI: What You Need to Know
Who Should Consider TAVI?
Determining the right candidate for TAVI involves assessing several factors:
- Severity of Aortic Stenosis: TAVI is primarily recommended for individuals with severe symptomatic aortic stenosis. Symptoms might include chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, or lightheadedness. It's essential that the condition is confirmed through diagnostic tests like echocardiography.
- Surgical Risk Assessment: Patients who are considered high or prohibitive risk for traditional open-heart surgery are prime candidates for TAVI. This includes elderly patients, those with multiple health issues, or individuals with conditions that make surgery particularly risky.
- Anatomical Considerations: The patient's aortic valve anatomy must be suitable for the TAVI procedure. Factors such as the size and shape of the aortic valve and the condition of the blood vessels used to access the heart are crucial.
- Life Expectancy and Quality of Life: Candidates should have a reasonable life expectancy and the potential for improved quality of life post-procedure. If severe comorbidities limit life expectancy or the ability to benefit from the procedure, TAVI might not be the best option.
What are the Benefits of TAVI?
TAVI offers several advantages, especially for those who are not ideal candidates for open-heart surgery:
- Minimally Invasive Approach: TAVI is performed through small incisions, reducing trauma to the chest and heart muscle. This approach often leads to shorter hospital stays and quicker recovery times.
- Symptom Relief: Many patients experience significant improvement in symptoms like chest pain and breathlessness shortly after the procedure, enhancing their quality of life.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: Compared to traditional surgery, TAVI is associated with a lower risk of infection and other complications, making it a safer alternative for high-risk patients.
How is the TAVI Procedure Performed?
Understanding the procedure can alleviate some concerns:
- Preparation: The patient undergoes thorough evaluations, including imaging tests, to plan the procedure. A multidisciplinary heart team assesses the patient's suitability for TAVI.
- Procedure: Under local anesthesia and mild sedation, a catheter is inserted through a small incision, usually in the groin. The new valve is guided through the catheter to the heart and positioned within the diseased aortic valve. Once in place, the new valve expands, pushing the old valve aside and starting to regulate blood flow immediately.
- Recovery: Most patients spend a short time in the hospital, often just a few days. Recovery is typically quicker than with open-heart surgery, allowing patients to return to their daily activities sooner.
What are the Potential Risks of TAVI?
While TAVI is generally safe, it's essential to be aware of potential risks:
- Need for a Pacemaker: Some patients may require a permanent pacemaker after the procedure due to changes in the heart's electrical system.
- Vascular Complications: There can be issues related to the blood vessels used to access the heart, such as bleeding or damage.
- Stroke: Though rare, there's a potential risk of stroke associated with the procedure.
It's crucial to discuss these risks with your cardiologist to make an informed decision.
TAVI vs. Traditional Surgery: How Do They Compare?
The choice between TAVI and surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) depends on various factors:
| Factor | TAVI | SAVR |
| Invasiveness | Minimally invasive; involves smaller incisions, often through the femoral artery, reducing physical trauma. | Requires open-heart surgery with a larger chest incision, leading to increased physical impact. |
| Recovery Time | Patients typically experience shorter hospital stays and quicker recovery periods. | Generally involves longer hospital stays and extended recovery times due to the nature of the surgery. |
| Durability | While TAVI has shown excellent outcomes, especially in high-risk patients, long-term durability data is still being evaluated. | SAVR has a long-established track record of durability, making it a preferred option for younger patients. |
| Risk of Complications | Lower risk of atrial fibrillation and acute kidney injury. However, there's a higher incidence of permanent pacemaker implantation and moderate-to-severe paravalvular regurgitation. | Higher risk of atrial fibrillation and acute kidney injury, but a lower incidence of permanent pacemaker implantation and paravalvular regurgitation. |
A team of cardiologists will assess individual patient factors to recommend the most suitable approach.
TAVI and Age: Who is it Right For?
Age is a key factor in deciding if Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) is the best treatment. For patients over 75, TAVI is often favored because it's less invasive, meaning quicker recovery and fewer risks than traditional surgery. 1 This is especially important for older individuals who may have other health issues. In the 65-75 age group, the choice between TAVI and surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) is more complex. Doctors consider overall health, anatomy, and patient preference. Both are options, and a heart team decides the best approach for each person. For those under 65, SAVR is usually recommended. Surgical valves have a proven long-term track record, important for younger patients who will likely live longer. While TAVI is promising, long-term data in younger people is still being gathered, making SAVR the current standard for this age group.
What Factors Influence the Choice Between TAVI and SAVR?
Several key factors influence the decision-making process:
- Valve Durability: Surgical valves have a proven track record of lasting durability, making them a reliable choice for younger patients.
- Surgical Risk: Patients with higher surgical risks due to other health issues may benefit more from the less invasive TAVI procedure.
- Anatomical Considerations: The specific anatomy of a patient's heart and blood vessels can impact the suitability of TAVI or SAVR.
- Patient Preference: Individual preferences regarding recovery times, potential risks, and lifestyle considerations play a significant role in the decision.
How is the Decision Between TAVI and SAVR Made?
The decision between TAVI and SAVR is individualized and includes thorough assessment by a multidisciplinary heart team. The team evaluates the patient's history, performs required imaging studies, and addresses the possible advantages and disadvantages of each procedure. Shared decision-making guarantees that the selected treatment suits the patient's health requirements and individual preferences.
Conclusion
Though TAVI has increased treatment for aortic stenosis, its applicability depends on age and individual health considerations.
In patients aged over 75, TAVI is usually the preferred procedure because of its minimally invasive procedure.
In the 65-75 age group, patients might opt for either TAVI or SAVE depending on certain situations. Patients younger than 65 are usually recommended to have SAVR, as surgical valves provide long-term durability. A proper assessment and consultation with a cardiologist are needed to decide the best treatment strategy for every patient.