What Your Period Blood Color Says About Your Health?
12/28/2024
Periods are a natural part of a woman’s life, but did you know the color of your period blood can provide insights into your health? From pink to black, the shade and consistency of menstrual blood can indicate hormonal changes, underlying medical conditions, or even your overall well-being. Understanding what your period blood color means is essential for maintaining reproductive and general health.
In this blog, we’ll explore the various period blood colors, what they signify, and when you should consider consulting a healthcare professional.
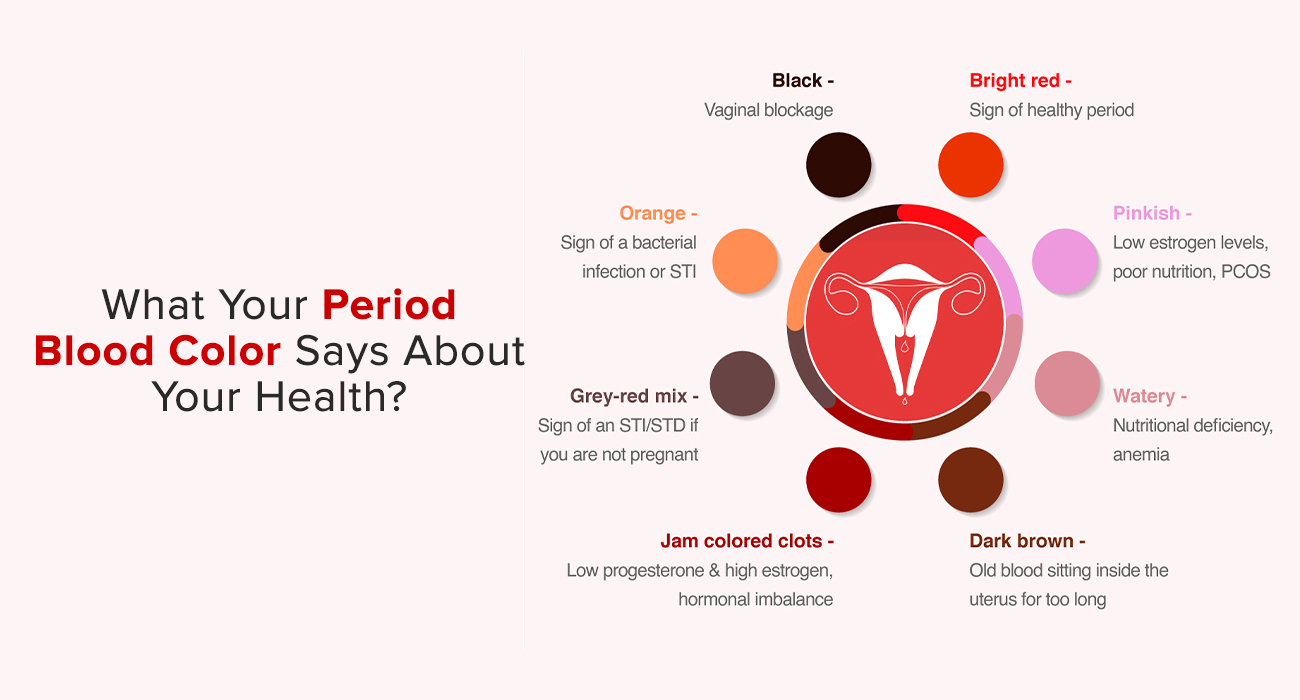
What Does the Color of Period Blood Mean?
Period blood color varies throughout your menstrual cycle, reflecting hormonal changes, uterine health, and blood flow speed. Here’s a breakdown of what different colors may indicate.
Pink Period Blood:
Pink period blood often occurs at the beginning or end of your cycle when the flow is lighter. It’s a mix of blood and cervical fluid, which gives it a diluted appearance.
Pink period blood can occur for several reasons. One possible cause is low estrogen levels, as estrogen helps thicken the uterine lining, and when levels are low, it can lead to lighter, pinkish blood. Another reason could be spotting or a light flow, where a very light period or spotting between cycles might cause the blood to appear pink. Additionally, pregnancy can be a factor, especially in early pregnancy, when implantation bleeding occurs, often manifesting as pinkish blood.
While pink period blood is usually harmless, persistent occurrences could indicate hormonal imbalances or pregnancy-related issues.
Bright Red Period Blood:
Bright red period blood is typically seen during the middle of your cycle when the flow is heaviest. This color signifies fresh blood being shed from the uterine lining.
Bright red period blood is often a sign of a healthy menstruation, indicating a regular and normal flow. However, if you notice persistent bright red blood outside of your period, it could be a sign of uterine fibroids or polyps, which are growths in the uterus that may cause abnormal bleeding. In some cases, bright red bleeding could also signal a miscarriage or injury, especially if it occurs outside of your normal menstrual cycle, requiring immediate attention and medical evaluation.
Dark Red Period Blood:
Dark red period blood usually appears later in the cycle or after lying down for a while. The darker hue indicates older blood that took longer to exit the uterus.
Dark red period blood can occur when the blood has a slower flow, meaning it has taken longer to leave the uterus, giving it time to oxidize and darken. Another possible cause is postpartum bleeding, which is common in women who have recently given birth as their uterus heals and sheds the remaining blood and tissue. Additionally, uterine fibroids can sometimes cause darker, heavier bleeding due to the growths within the uterus, leading to altered menstrual flow and blood color.
Dark red blood during periods is usually normal but should be monitored if accompanied by unusual symptoms like extreme pain or clotting.
Brown Period Blood Turn:
Brown period blood is a common occurrence, especially at the start or end of a cycle when the flow is lighter. This color indicates older blood that has had time to oxidize.
Brown period blood is often a result of the end of your period, when the blood flow slows down, and older blood has more time to oxidize, turning it brown. Another possible cause is pregnancy spotting, which can occur in early pregnancy and might appear as brown discharge, often related to implantation. Additionally, women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) may experience irregular cycles and brown spotting, which is linked to hormonal imbalances that affect the menstrual flow.
While brown blood is generally not a concern, it could signal conditions like PCOS or infection if accompanied by irregular cycles or discomfort.
Black Period Blood:
Black period blood might look alarming, but it’s often a sign of very old blood that took a long time to leave the uterus.
Black blood during periods is typically older blood, which has had more time to oxidize, turning it a darker color. This can happen if the blood takes longer to leave the body, especially at the beginning or end of a period. In some rare cases, vaginal blockage could cause black blood, as it may indicate an obstruction in the vaginal canal, leading to retained blood. Additionally, if the black blood has a foul odor, it could be a sign of an infection, and medical attention should be sought to diagnose and treat the issue.
Dark Brown Period Blood:
Dark brown period blood is a deeper shade than the typical brown and often seen at the very end of a period.
Dark brown blood is often linked to the end of the menstrual cycle, as the uterine lining fully sheds, and the blood flow slows down, resulting in older blood that appears brown. In some cases, pregnancy or miscarriage can cause brown spotting, especially during early pregnancy. If the spotting is accompanied by cramping or a significant change in flow, it could be an early sign of a miscarriage. Infections or STDs can also lead to dark brown blood, often accompanied by a strong odor, and may require medical attention to diagnose and treat the underlying infection.
What Do Blood Clots in Period Blood Indicate?
Blood clots during menstruation are common and often harmless, especially during heavy flow days. However, they can sometimes indicate an underlying issue.
Blood clots during your period can occur for several reasons. One common cause is a heavy flow, where the uterus sheds its lining quickly, leading to the formation of large blood clots. Conditions like fibroids or endometriosis can also result in abnormal clotting, as these conditions often cause heavier and more irregular periods.
Additionally, miscarriage can lead to blood clots during pregnancy, especially if the clots are accompanied by pain or heavy bleeding. If blood clots are frequent or cause significant discomfort, it's important to consult a gynecologist for proper evaluation and treatment.
Clots larger than a quarter in size should be discussed with a gynaecologist.
Also, read: What are the Reasons for Late Period with a Negative Pregnancy Test?
How Much Blood is Lost During a Period?
Understanding how much blood loss is normal during a period is crucial for assessing menstrual health.
- Normal blood loss: On average, women lose about 30-40 milliliters of blood during their period.
- Heavy bleeding: Blood loss exceeding 80 milliliters may indicate menorrhagia, a condition that can lead to anemia.
If you frequently change pads or tampons within two hours or notice significant clots, consult a doctor.
When Should You Consult a Doctor About Period Blood Color?
While variations in period blood color are usually harmless, certain signs warrant medical attention:
- Consistently heavy bleeding or passing large clots.
- Unusual colors like black or foul-smelling discharge.
- Persistent spotting between periods.
- Painful or irregular cycles.
How to Maintain Menstrual Health?
Maintaining menstrual health involves understanding your cycle and addressing any irregularities promptly. Here are some tips:
- Track your period: Apps or journals can help identify patterns or abnormalities.
- Stay hydrated: Proper hydration helps maintain smooth blood flow.
- Eat a balanced diet: Foods rich in iron and vitamins support overall menstrual health.
- Consult a gynecologist: Regular check-ups can help detect issues early.
Conclusion
The color of your period blood offers valuable clues about your reproductive health. From pink to black, each shade reflects different factors, from hormonal changes to potential health concerns. While most variations are normal, persistent abnormalities should prompt a consultation with a healthcare professional. Understanding what your period blood color means empowers you to take charge of your menstrual health and ensure your overall well-being.
If you notice significant changes in your period blood color or experience symptoms like excessive bleeding or pain, reach out to a gynaecologist for guidance.